Thermoplastic Tank Calculator

Description
A spreadsheet for estimating wall thickness of thermoplastic (Polyethylene/Polypropylene) tanks made by helix winding or sheet lamination. Based upon DVS2205 (largely superseded by a European Std) the design principle is based on creep of the polymer. Verified by comparison with existing tanks & used to assess and estimate correctness of tank design.
All tank design procedures are required to take into account materials compatibility, working temperatures, anticipated loading by the contents, wind and seismic factors and must also define a design life. For metallic tanks an allowable stress in the wall is calculated;
reduction of wall thickness due to corrosion will increase the working stress and thus service life is defined by an allowable loss in wall thickness. Designers of GRP tanks will define the service life by the number of fill / empty cycles as cyclic loading causes fracture of glass fibres and the resin. Thermoplastic tanks use creep deformation as the design basis for service life.
Materials compatibility of thermoplastics allows their use for a very broad range ofchemicals and they are often used to minimise product contamination which even a small amount of corrosion of a metallic tank could cause. Thermoplastics are, in general, not
brittle and are less prone to catastrophic failure. The main drawbacks when compared with other materials are:
• thermoplastics are inherently weaker and therefore require a much thicker construction than GRP or metals which limits the size of tank which can be fabricated.
• thermoplastics tend to loose strength very rapidly with temperature which limits the maximum allowable operating temperature
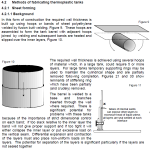
DVS 2205 is based upon creep of the material, i.e. permanent strain or ‘stretching’ over a period of time, under constant load, until failure occurs. The results of tests on pipes are presented in a series of creep strength curves as a function of temperature and time for a particular grade of thermoplastic materials. This type of graph is used by the tank designer to establish the creep strength at the design temperature for the required design life. For example for a design temperature of 20°C and a design life of 10 years the creep strength, K is ~8.4 N.mm-2.
Reference: http://www.hse.gov.uk/research/hsl_pdf/2006/hsl0621.pdf
Calculation Reference
Design with Thermoplastics
Design with Polymers
DVS 2205
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.