Fatigue Damage in Steel Welds.xls

Description
Calculate fatigue damage in a steel weld subjected to constant amplitude loading and variable amplitude loading. Based on methods described in the references below.
Calculation Reference
Gene Mathers from TWI has written an overview of fatigue.
Use with the efatigue weld classification finder.
Guidance on how to select joint classifications can be found online in "Fatigue strength of welded structures" - Google Books Result
by Stephen John Maddox - 1991 - Technology & Engineering - 198 pages
Joint classification For the purposes of fatigue design each part of a welded ... Different details are combined in a single class on the basis that they ...
Fatigue of Welded Structures - Gurney
BS7608 Fatigue Design of Steel Structures
This document outlines the methodology for calculating fatigue damage in steel welds under both constant amplitude loading (CAL) and variable amplitude loading (VAL) conditions, based on established standards and industry practices.
Joint Classification
The first step is proper classification of the welded joint:
- Identify the basic joint geometry (butt, fillet, cruciform, etc.)
- Consider loading direction relative to weld orientation
- Account for potential stress concentrations
- Determine the appropriate BS7608 classification class (from Class B to Class W)
- Note any specific fabrication requirements that affect classification
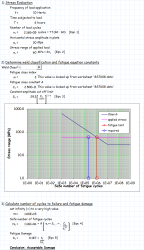
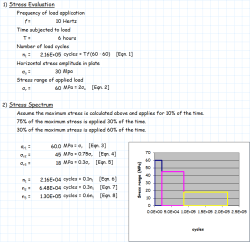
Stress Analysis
Constant Amplitude Loading (CAL)
For constant amplitude loading, determine:
- Nominal stress range (Δσ)
- Mean stress (σm)
- Stress ratio (R)
- Number of cycles (N)
Variable Amplitude Loading (VAL)
For variable amplitude loading:
- Obtain stress-time history
- Perform rainflow counting to identify stress cycles
- Create stress range histogram
- Consider mean stress effects if significant
Fatigue Damage Calculation
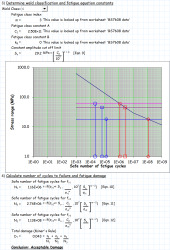
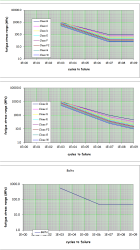
S-N Curve Selection
- Select appropriate S-N curve based on:
- Joint classification
- Environmental conditions
- Loading conditions
- Safety requirements
Damage Calculation Methods
For Constant Amplitude Loading:
- Calculate cycles to failure (Nf) using S-N curve: log(Nf) = log(C) - m×log(Δσ) where:
- C = fatigue strength coefficient
- m = slope of S-N curve
- Δσ = stress range
- Calculate damage (D): D = n/Nf where:
- n = applied cycles
- Nf = cycles to failure
For Variable Amplitude Loading:
- Apply Miner's Rule for cumulative damage: D = Σ(ni/Nfi) where:
- ni = number of cycles at stress range i
- Nfi = cycles to failure at stress range i
Safety Factors
Apply appropriate safety factors considering:
- Consequence of failure
- Access for inspection
- Environmental conditions
- Loading uncertainty
- Material variability
Acceptance Criteria
- For safe design: D ≤ 1.0
- Consider lower values (e.g., D ≤ 0.5) for critical applications
- Account for any specific requirements from applicable standards
Special Considerations
Environmental Effects
- Corrosive environments
- Temperature effects
- Coating protection
- Maintenance requirements
Manufacturing Quality
- Weld profile requirements
- NDT requirements
- Post-weld treatments if applicable
- Quality control measures
Documentation Requirements
- Design calculations
- Joint classification justification
- Loading assumptions
- Material certificates
- Welding procedure specifications
- Inspection records
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.