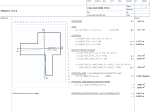
Properties of a general polygon

Description
Calculation of the perimeter length, area, centroid, second moment of areas, principal axes and distance to the outer fibres of any plane non-intersecting polygon using Gauss's area method ('shoelace method') from the cartesian coordinates of the perimeter. Set up for SI units, but can be used for Imperial. General application derived from use in civil and structural engineering for irregular foundations and sections in bending.
Gauss's area method, also known as the 'shoelace method,' is a technique for calculating the area of a non-intersecting polygon from its Cartesian coordinates. It can also be extended to compute the perimeter length, centroid, second moment of areas, principal axes, and distance to the outer fibers of the polygon. Here's a summary of the steps involved:
-
Perimeter length: Calculate the distance between each consecutive pair of vertices and sum them up to find the perimeter length.
-
Area: To find the area using the shoelace method, list the coordinates of the polygon vertices in a clockwise or counterclockwise order. Multiply the x-coordinate of each vertex by the y-coordinate of the next vertex, sum these products, and subtract the sum of the products obtained by multiplying the y-coordinate of each vertex by the x-coordinate of the next vertex. Divide the absolute value of the resulting number by 2 to get the area.
-
Centroid: The centroid coordinates (Cx, Cy) are calculated by dividing the sum of the products of the consecutive vertices' x- and y-coordinates by six times the area.
-
Second moment of areas: Calculate the second moment of areas (Ixx, Iyy, and Ixy) using the vertex coordinates and the area of the polygon.
-
Principal axes: Compute the principal axes using the second moment of areas (Ixx, Iyy, and Ixy). The angle between the principal axes and the coordinate axes can be found using the arctangent function.
-
Distance to outer fibers: To calculate the distance to the outer fibers, determine the maximum and minimum distances between the centroid and the vertices of the polygon along the principal axes.
Using Gauss's area method, you can efficiently calculate various properties of any plane non-intersecting polygon using the Cartesian coordinates of its perimeter vertices. This approach is useful in various applications, such as structural engineering, computer graphics, and geographic information systems.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.