DKE_PipingVibration_MainLines.xlsx

Description
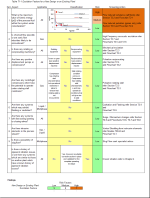
EI Guidelines for the Avoidance of Vibration - TM-01 Qualitative Assessment
Energy Institute Guidelines for the Avoidance of Vibration Induced Fatigue Failure in Process Pipework (Second Edition Jan 2008)
Technical Module TM-01 Qualitative Assessment
TM-01 is one of several technical modules (TM-01 through TM-12) used in Proactive and Reactive vibration assessment of piping systems
TM-01 is applied primarily to main lines within a piping system to identify the need for and then prioritise further risk assessment actions
TM-01 can be applied to i) New Designs, ii) Existing Plants not previously assessed and iii) Changes to previously assessed Existing Plants
Calculation Reference
Pipe Vibration
Pipe Fatigue
Avoidance of Vibration
The Energy Institute (EI) has published guidelines for the avoidance of vibration-induced fatigue failure in process pipework. These guidelines provide a comprehensive methodology for identifying, assessing, and mitigating vibration risks in process pipework systems, with the aim of reducing the likelihood of fatigue failures and improving the safety and reliability of the facilities. The EI guidelines can be summarized in the following steps:
-
Data collection and screening: Gather information about the process pipework system, including its design, layout, materials, operating conditions, and any history of vibration issues. Perform an initial screening to identify areas of potential concern based on factors such as flow rates, pressure drops, and excitation sources (e.g., pumps, compressors, or control valves).
-
Detailed assessment and measurement: Perform a detailed assessment of the identified areas of concern, using techniques such as vibration measurement, strain gauge monitoring, and finite element analysis. This may involve measuring the actual vibration levels in the pipework system and comparing them to the acceptable limits defined in the EI guidelines.
-
Vibration risk evaluation: Evaluate the risk of vibration-induced fatigue failure in the pipework system, considering factors such as the measured vibration levels, the number of stress cycles, and the fatigue strength of the materials. This risk evaluation can help prioritize areas for further investigation or mitigation measures.
-
Root cause analysis: Identify the root causes of any excessive vibration in the pipework system, which may include factors such as flow-induced turbulence, mechanical resonance, or insufficient support. A thorough root cause analysis can help guide the selection of appropriate mitigation measures.
-
Mitigation measures: Develop and implement mitigation measures to address the identified vibration risks, which may include:
- Modifying the process conditions (e.g., adjusting flow rates or pressures)
- Redesigning or modifying the pipework layout (e.g., adding bends, loops, or expansion joints)
- Enhancing the pipework support system (e.g., adding or adjusting supports, clamps, or restraints)
- Adding vibration dampers or isolators
- Implementing active vibration control systems
-
Monitoring and maintenance: Establish a monitoring and maintenance program to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the mitigation measures and to detect any new or emerging vibration risks. This may involve periodic vibration measurements, visual inspections, and the use of condition monitoring technologies such as accelerometers or strain gauges.
By following the Energy Institute guidelines for the avoidance of vibration-induced fatigue failure in process pipework, operators can reduce the risk of fatigue failures, improve the safety and reliability of their facilities, and minimize the potential for costly downtime and repairs.
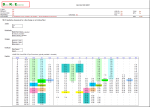
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.