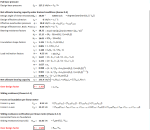
Drained Strip Foundation En1997

Description
STRIP FOUNDATION (EN1997-1:2004)
Purpose of calculation
Design and alalysis of two leaf block basic strip foundation on a ridgid concrete base.
Calculation Reference
TEDDS Trial Software calulation version 3.1.04 - BS EN1997-1:2004 incorporating Corrigendum dated
February 2009 and the UK NA incorporating Corrigendum No.1.
Calculation Validation
Calculations checked by P.J.
Strip foundation details - considering a one metre strip
Length of foundation
Width of foundation
Foundation area
Depth of foundation
Depth of block work
Depth of soil over foundation
Level of water
Density of water
Density of block
Density of concrete
Cavity details
Width of cavity
Wall no.1 details
Width of wall
Position in y-axis
Wall no.2 details
Width of wall
Position in y-axis
Soil Properties
Density of Soil
Characteristic cohesion
Charac. angle of shear resistance
Characteristic friction angle
Foundation loads
Self weight
Soil Weight
Wall no.1 loads per linear metre
Self weight
Variable load in y-axis
Permanent load in y-axis
Variable load in z-axis
Permanent load in z-axis
Surcharge next to wall z-axis
Wall no.2 loads per linear metre
Self weight
Variable load in y-axis
Permanent load in y-axis
Variable load in z-axis
Permanent load in z-axis
Surcharge next to wall z-axis
Calculation Reference
Foundation Calculations
Soil Mechanics
Building Calculations
A strip foundation is a type of shallow foundation commonly used in construction to support linear structures like walls, columns, or rows of columns. The main purpose of a strip foundation is to distribute the load from the supported structure evenly across the ground, preventing excessive settlement and ensuring stability.
EN 1997-1:2004, also known as Eurocode 7 - Geotechnical Design - Part 1: General Rules, provides guidelines for the geotechnical aspects of the design of civil engineering works and buildings, including foundations. For designing a strip foundation, Eurocode 7 should be used in conjunction with Eurocode 2 (EN 1992) for the design of concrete structures.
When designing a strip foundation using EN 1997-1:2004, the following steps are typically followed:
-
Site investigation: Assess the ground conditions, soil properties, and groundwater levels to determine the bearing capacity and settlement characteristics of the soil.
-
Load determination: Calculate the loads imposed by the structure on the foundation, including dead loads, live loads, and any additional loads such as wind or seismic loads.
-
Bearing capacity and settlement analysis: Analyze the bearing capacity of the soil to ensure that the foundation will not fail due to shear or punching. Assess the potential settlement of the foundation to ensure that it will not cause excessive differential settlement or structural damage.
-
Foundation dimensions: Determine the width, depth, and length of the strip foundation based on the load distribution, bearing capacity, and settlement analysis.
-
Reinforcement design: Design the reinforcement for the strip foundation, considering the bending moments, shear forces, and axial loads, as per Eurocode 2 (EN 1992) guidelines.
-
Detailing and construction: Prepare detailed drawings and specifications for the strip foundation, including reinforcement details, dimensions, and construction materials.
-
Quality control and monitoring: Implement quality control measures during construction, and monitor the performance of the foundation after construction to ensure it meets the design requirements.
Remember that local building regulations and codes may also apply, so it's essential to consult with local authorities and engineers familiar with the region's specific requirements.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.