Cantilever retaining wall analysis.xls

Description
Purpose of calculation: The details of a cantilever retaining wall are shown below, is the design of the wall satisfactory?
Calculation Reference: Craig Soil Mechanics. R.F. Craig
Calculation Validation: Check against a worked example in the reference above.
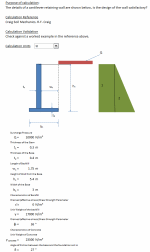
Calculation Parameters
Surcharge Pressure
Thickness of the Stem
Thickness of the Base
Length of Backfill
Height of Wall from the Base
Width of the Base
Characteristics of Backfill
Drained (effective stress) Shear Strength Parameter
Unit Weight of the backfill
Drained (effective stress) Shear Strength Parameter
Characteristics of Concrete
Unit Weight of Concrete
Angle of friction between the base and the foundation soil is
Active earth pressure coefficient
Horizontal Forces
Sum of Horizontal Forces
Vertical Forces
Sum of Vertical Forces
Lever
Moments
Lever arm of base resultant
FoS against overturning
Eccentricity of base reaction
Maximum and minimum base pressures
FoS against sliding
Calculation Reference
Geotechnics
Soil Mechanics
Craig's Soil Mechanics
The analysis of a cantilever retaining wall following Craig's Soil Mechanics involves the following steps:
- Determine the soil properties, such as the soil type, unit weight, angle of internal friction, and cohesion.
- Determine the dimensions of the retaining wall, including the height, base width, and toe length.
- Determine the design loads, which include the soil pressure, water pressure, surcharge loads, and any other loads that may act on the wall.
- Determine the depth and width of the foundation required to support the wall.
- Calculate the active earth pressure using one of the following methods: a. Coulomb's wedge theory, which assumes that the soil above the wall moves as a wedge. b. Rankine's theory, which assumes that the soil above the wall moves as a block. c. The pressure distribution method, which assumes that the soil pressure varies linearly with depth.
- Calculate the passive earth pressure using one of the following methods: a. Coulomb's theory, which assumes that the soil below the wall is stationary. b. Rankine's theory, which assumes that the soil below the wall is mobilized.
- Determine the required reinforcing steel for the retaining wall based on the design loads and the wall dimensions.
- Prepare construction specifications and drawings for the retaining wall.
The analysis of a cantilever retaining wall can be further refined by considering other factors, such as the presence of groundwater, the effect of soil stratification, and the effect of soil consolidation. The analysis can also be performed using computer software or spreadsheet programs, which can provide more accurate and efficient results.
Overall, the analysis of a cantilever retaining wall following Craig's Soil Mechanics provides a rigorous and systematic approach to design and construct retaining walls that can support the required loads and ensure the stability and safety of the structures.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.