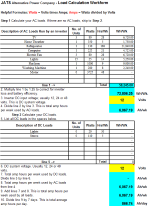
Photovoltaic Design

Description
Load Calculation
Solar Array Sizing
Battery Sizing
How green could you make your house?
Calculation Reference
Photovoltaic Design
Solar Array Sizing
Battery Sizing
With the four given parameters (terminal voltage, terminal resistance, no-load speed, and no-load current), you can estimate the performance of a DC or brushless DC motor by calculating its efficiency, torque, and power output under specific operating conditions.
- Terminal Voltage (V)
- Terminal Resistance (R)
- No-Load Speed (ωo, in RPM)
- No-Load Current (Io)
First, let's calculate the motor's speed-torque slope and no-load losses:
-
Speed-Torque Slope (K): K = (ωo * R) / V
-
No-Load Losses (P_loss): P_loss = Io * V
Now, you can calculate the motor's performance at a specific operating current (I):
-
Operating Current (I): Choose a value representing the current under specific operating conditions.
-
Voltage Drop (V_drop): V_drop = I * R
-
Back EMF (E): E = V - V_drop
-
Operating Speed (ω, in RPM): ω = E / K
-
Operating Torque (T): T = (V - E) * K / R
-
Electrical Power Input (P_in): P_in = V * I
-
Mechanical Power Output (P_out): P_out = T * ω * (π / 30) (Convert RPM to rad/s by multiplying by π/30)
-
Efficiency (η): η = P_out / P_in * 100%
Using these calculations, you can estimate the motor's performance under specific operating conditions. Keep in mind that these calculations are simplified and may not be entirely accurate, as they do not account for factors like magnetic saturation, temperature effects, or complex motor dynamics. However, they can provide a reasonable approximation of the motor's performance and efficiency.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.